A C System Vehicle Inspection Obd Reading
Need a simple, practical intro to OBD2?
In this guide we introduce the On Lath Diagnostic (OBD2) protocol incl. the OBD2 connector, OBD2 parameter IDs (PID) and the link to CAN motorbus.
Note: This is a practical intro so you lot will also learn how to request and decode OBD2 information, key logging use cases and practical tips.
Encounter below why this has become the #1 OBD2 tutorial.
You can also check out our OBD2 intro video above (150K+ views on YouTube)
What is OBD2?
In brusque, OBD2 is your vehicle'southward built-in cocky-diagnostic organization.
Yous've probably encountered OBD2 already:
Ever noticed the malfunction indicator light on your dashboard?
That is your car telling you there is an issue. If y'all visit a mechanic, he will use an OBD2 scanner to diagnose the issue.
To practice and so, he will connect the OBD2 reader to the OBD2 sixteen pin connector near the steering wheel.
This lets him read OBD2 codes aka Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) to review and troubleshoot the issue.


The OBD2 connector
The OBD2 connector lets y'all admission data from your auto hands. The standard SAE J1962 specifies two female OBD2 sixteen-pin connector types (A & B).
In the analogy is an example of a Type A OBD2 pivot connector (likewise sometimes referred to as the Data Link Connector, DLC).
A few things to note:
- The OBD2 connector is about your steering wheel, but may be hidden behind covers/panels
- Pin sixteen supplies battery power (often while the ignition is off)
- The OBD2 pinout depends on the advice protocol
- The most mutual protocol is CAN (via ISO 15765), meaning that pins 6 (Can-H) and 14 (Tin can-Fifty) volition typically be continued
OBD2 connector - blazon A vs. B
In practise, y'all may encounter both the type A and type B OBD2 connector. Typically, type A will be establish in cars, while blazon B is mutual in medium and heavy duty vehicles.
As evident from the illustration, the two types share similar OBD2 pinouts, simply provide two different power supply outputs (12V for type A and 24V for type B). Often the baud rate will differ as well, with cars typically using 500K, while virtually heavy duty vehicles use 250K (more recently with support for 500K).
To aid physically distinguish between the 2 types of OBD2 sockets, note that the type B OBD2 connector has an interrupted groove in the centre. As a result, a blazon B OBD2 adapter cable volition be compatible with both types A and B, while a type A volition not fit into a type B socket.

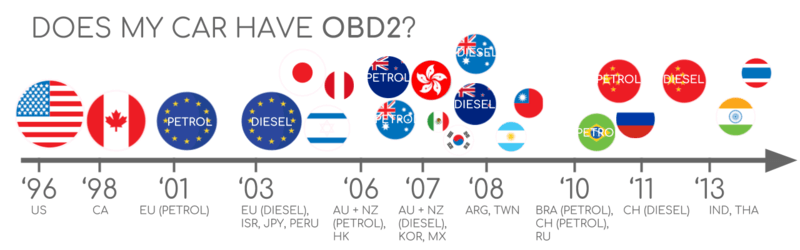
Does my car have OBD2?
In short: Probably!
Well-nigh all newer cars support OBD2 and most run on Tin can (ISO 15765). For older cars, exist enlightened that even if a xvi pin OBD2 connector is nowadays, it may still non support OBD2. One way to determine compliance is to place where & when it was bought new:
Link betwixt OBD2 and Tin bus
On board diagnostics, OBD2, is a 'higher layer protocol' (like a linguistic communication). Tin is a method for advice (like a phone).
In item, the OBD2 standard specifies the OBD2 connector, incl. a set of 5 protocols that it tin can run on (encounter beneath). Further, since 2008, Tin can motorbus (ISO 15765) has been the mandatory protocol for OBD2 in all cars sold in the The states.


What is the ISO 15765 standard?
ISO 15765 refers to a set up of restrictions applied to the Tin standard (which is itself defined in ISO 11898). One might say that ISO 15765 is like "CAN for cars".
In particular, ISO 15765-four describes the physical, data link layer and network layers, seeking to standardize the Tin can charabanc interface for external test equipment. ISO 15765-2 in turn describes the transport layer (ISO TP) for sending CAN frames with payloads that exceed eight bytes. This sub standard is likewise sometimes referred to every bit Diagnostic Advice over CAN (or DoCAN). See also the 7 layer OSI model analogy.
OBD2 can besides be compared to other higher layer protocols (east.1000. J1939, CANopen).
The five OBD2 protocols
As explained above, Can motorbus today serves equally the basis for OBD2 advice in the vast majority of cars through ISO 15765.
Notwithstanding, if you lot're inspecting an older motorcar (pre 2008), it is useful to know the other 4 protocols that have been used as basis for OBD2. Notation too the pinouts, which can be used to make up one's mind which protocol may be used in your automobile.
- ISO 15765 (Tin bus): Mandatory in United states cars since 2008 and is today used in the vast majority of cars
- ISO14230-iv (KWP2000): The Keyword Protocol 2000 was a mutual protocol for 2003+ cars in due east.k. Asia
- ISO9141-ii: Used in EU, Chrysler & Asian cars in 2000-04
- SAE J1850 (VPW): Used by and large in older GM cars
- SAE J1850 (PWM): Used generally in older Ford cars

Below we list some of the nearly relevant SAE/ISO standards related to OBD2:
SAE J1962: This standard defindes the physical connector used for the OBD2 interfacing, i.e. the OBD2 connector. The standard describes both the vehicle OBD2 connector and the connector used by the external exam equipment (due east.yard. an OBD2 scanner or OBD2 information logger). In particular, the standard dictates the location and access to the OBD2 connector.
SAE J1979: The SAE J1979 standard describes the methods for requesting diagnostic information via the OBD2 protocol. It also includes a list of standardized public OBD2 parameter IDs (OBD2 PIDs) that automotive OEMs may implement in cars (though they are non required to do then). Vehicle OEMs may also determine to implement additional proprietary OBD2 PIDs across those outlined past the SAE J1979 standard.
SAE J1939: The J1939 standard describes the data protocol used for heavy-duty vehicle communication. While OBD2 PID data is only available on-asking by OBD2 test equipment, the J1939 protocol is used in most heavy-duty vehicles equally the basic means for communicating CAN traffic - meaning data is broadcast continuously.
ISO 11898: This standard describes the Tin coach data link layer and physical layer, serving every bit the basis for OBD2 communication in nigh cars today
ISO 15765-2: The ISO-TP standard describes the 'Ship Layer', i.e. how to send data packets exceeding 8 bytes via CAN bus. This standard is important as it forms the basis for Unified Diagnostic Services (UDS) advice, which relies on sending multiframe Tin data packets.
ISO 14229: This describes UDS communication in particular
OBD2 history
OBD2 originates from California where the California Air Resources Board (CARB) required OBD in all new cars from 1991+ for emission control purposes.
The OBD2 standard was recommended by the Lodge of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and standardized DTCs and the OBD connector across manufacturers (SAE J1962).
From there, the OBD2 standard was rolled out step-by-step:
- 1996: OBD2 made mandatory in USA for cars/light trucks
- 2001: Required in Eu for gasoline cars
- 2003: Required in EU also for diesel fuel cars (EOBD)
- 2005: OBD2 was required in Us for medium duty vehicles
- 2008: The states cars must utilise ISO 15765-4 (CAN) as OBD2 ground
- 2010: Finally, OBD2 was required in US heavy duty vehicles



OBD2 future
OBD2 is here to stay - but in what form?
Two potential routes may radically change OBD2:
In today'south world of continued cars, OBD2 tests can seem cumbersome: Manually doing emission control checks is time-consuming and expensive.
The solution? OBD3 - adding telematics to all cars.
Basically, OBD3 adds a small-scale radio transponder (as in e.g. bridge tolls) to all cars. Using this, the automobile vehicle identification number (VIN) and DTCs can exist sent via WiFi to a central server for checks.
Many devices today already facilitate transfer of CAN or OBD2 data via WiFi/cellular - e.grand. the CANedge2 WiFi Tin can logger.
This saves cost and is user-friendly, but it is besides politically a challenge due to surveillance concerns.
The OBD2 protocol was originally designed for stationary emission controls.
Yet, today OBD2 is used extensively for generating existent-fourth dimension data past 3rd parties - via OBD2 dongles, CAN loggers etc. However, the High german car industry is looking to change this:
OBD has been designed to service cars in repair shops. In no manner has it been intended to allow 3rd parties to build a class of data-driven economic system on the access through this interface"
- Christoph Grote, SVP Electronics, BMW (2017)
The proposal is to "turn off" the OBD2 functionality while driving - and instead collect the information in a central server. This would effectively put the manufacturers in command of the automotive 'big information'.
The argumentation is based in security (e.g. removing the risk of car hacking), though many see it equally a commercial movement. Whether this becomes a real trend is to be seen - only information technology may truly disrupt the marketplace for OBD2 3rd political party services.

OBD2 parameter IDs (PID)
Why should you care about OBD2 data?
Mechanics manifestly care about OBD2 DTCs (maybe you do too), while regulatory entities need OBD2 to control emission.
But the OBD2 protocol too supports a broad range of standard parameter IDs (PIDs) that can exist logged across most cars.
This means that you can easily get human-readable OBD2 data from your car on speed, RPM, throttle position and more.
In other words, OBD2 lets you analyze data from you car easily - in contrast to the OEM specific proprietary raw CAN data.
In principle information technology is uncomplicated to log the raw Tin can frames from your motorcar. If you e.g. connect a Can logger to the OBD2 connector, you lot'll start logging broadcasted Can bus data out-the-box. However, the raw CAN messages need to be decoded via a database of conversion rules (DBC) and a suitable CAN software that supports DBC decoding (like due east.chiliad. asammdf). The challenge is that these CAN DBC files are typically proprietary, making the raw CAN data unreadable unless you're the automotive OEM.
Car hackers may effort to reverse engineer the rules, though this can be hard. CAN is, however, still the only method to get "full access" to your motorcar information - while OBD2 simply provides access to a limited subset of information.


How to log OBD2 data?
OBD2 data logging works as follows:
- You connect an OBD2 logger to the OBD2 connector
- Using the tool, you lot send 'asking frames' via CAN
- The relevant ECUs transport 'response frames' via Tin can
- Decode the raw OBD2 responses via due east.thousand. an OBD2 DBC
In other words, a Can logger that is able to transmit custom Can frames can as well be used every bit an OBD2 logger.
Note that cars differ by model/year in what OBD2 PIDs they support. For details, run across our OBD2 information logger guide.
CANedge OBD2 data logger
The CANedge lets you easily log OBD2 data to an 8-32 GB SD bill of fare. Simply specify what OBD2 PIDs you wish to asking, then connect it to your automobile via an OBD2 adapter to first logging. Process the information via free software/APIs and our OBD2 DBC.
learn more
Raw OBD2 frame details
To go started recording OBD2 information, information technology is helpful to understand the basics of the raw OBD2 message structure. In simplified terms, an OBD2 message is comprised of an identifier and data. Further, the data is split in Mode, PID and data bytes (A, B, C, D) as below.

Identifier: For OBD2 messages, the identifier is standard eleven-fleck and used to distinguish between "request letters" (ID 7DF) and "response messages" (ID 7E8 to 7EF). Annotation that 7E8 volition typically be where the main engine or ECU responds at.
Length: This simply reflects the length in number of bytes of the remaining data (03 to 06). For the Vehicle Speed example, information technology is 02 for the asking (since just 01 and 0D follow), while for the response it is 03 as both 41, 0D and 32 follow.
Manner: For requests, this will exist between 01-0A. For responses the 0 is replaced by four (i.e. 41, 42, … , 4A). There are ten modes as described in the SAE J1979 OBD2 standard. Mode 1 shows Current Data and is e.one thousand. used for looking at real-fourth dimension vehicle speed, RPM etc. Other modes are used to eastward.thousand. show or clear stored diagnostic trouble codes and bear witness freeze frame information.
PID: For each way, a list of standard OBD2 PIDs exist - east.m. in Manner 01, PID 0D is Vehicle Speed. For the total list, check out our OBD2 PID overview. Each PID has a description and some take a specified min/max and conversion formula.
The formula for speed is due east.g. but A, meaning that the A data byte (which is in HEX) is converted to decimal to get the km/h converted value (i.due east. 32 becomes fifty km/h above). For e.g. RPM (PID 0C), the formula is (256*A + B) / 4.
A, B, C, D: These are the information bytes in HEX, which demand to exist converted to decimal form earlier they are used in the PID formula calculations. Notation that the terminal information byte (afterward Dh) is not used.
OBD2 asking/response case
An instance of a request/response CAN message for the PID 'Vehicle Speed' with a value of 50 km/h can be seen in the analogy.
Note in item how the formula for the OBD2 PID 0D (Vehicle Speed) just involves taking the 4th byte (0x32) and converting it to decimal form (50).
In some vehicles (e.m. vans and calorie-free/medium/heavy duty vehicles), you lot may find that the raw Tin can data uses extended 29-fleck CAN identifiers instead of 11-bit CAN identifiers.
In this instance, you volition typically need to change the OBD2 PID requests to use the Tin ID 18DB33F1 instead of 7DF. The data payload structure is kept identical to the examples for 11-bit CAN IDs.
If the vehicle responds to the requests, yous'll typically see responses with Tin IDs 18DAF100 to 18DAF1FF (in practice, typically 18DAF110 and 18DAF11E). The response identifier is also sometimes shown in the 'J1939 PGN' grade, specifically the PGN 0xDA00 (55808), which in the J1939-71 standard is marked as 'Reserved for ISO 15765-two'.
We provide an OBD2 DBC file for both the xi-bit and 29-chip responses, enabling simple decoding of the data in about Can software tools.



The 10 OBD2 services (aka modes)
There are 10 OBD2 diagnostic services (or modes) as described in the SAE J1979 OBD2 standard. Mode 1 shows Current Information and is used for looking at real-time parameters similar vehicle speed, RPM, throttle position etc. Other modes are e.g. used to show/clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and show freeze frame data.
Manufacturers practice not have to back up all diagnostic services - and they may support modes outside these 10 services (i.e. manufacturer specific OBD2 services).
OBD2 data logging - use case examples
OBD2 data from cars and light trucks tin be used in various employ cases:

Logging information from cars
OBD2 data from cars can due east.grand. be used to reduce fuel costs, improve driving, test paradigm parts and insurance
Learn more

Real-time machine diagnostics
OBD2 interfaces can exist used to stream man-readable OBD2 information in existent-time, e.yard. for diagnosing vehicle issues
Larn more

Predictive maintenance
Cars and light trucks can be monitored via IoT OBD2 loggers in the deject to predict and avoid breakdowns
Learn more than

Vehicle blackbox logger
An OBD2 logger can serve equally a 'blackbox' for vehicles or equipment, providing data for east.one thousand. disputes or diagnostics
Acquire more
Do you have an OBD2 data logging employ case? Reach out for free sparring!
Contact us
Beneath we outline the almost common OBD2 analyzer categories:
OBD2 scanners: Used every bit car diagnostic tools in static reading/clearing of DTCs by e.g. mechanics. An OBD2 browse tool is typically used in diagnosing vehicle issues e.g. indicated by an activated MIL. Various types exist and some private persons utilise low cost variants as elementary machine code readers for self-diagnosing their automobile health.
Bluetooth OBD2 dongles: Many OBD2 bluetooth dongles exist, which let yous view car information direct on your smartphone via an app. Typically OBDII bluetooth dongles are low cost and easy-to-employ, though likewise limited in terms of their usability outside the bluetooth-to-app visualization purpose. The purpose of an OBD2 bluetooth dongle is typically to monitor personal driving behavior and vehicle health.
OBD2 interfaces: Provide real-time OBD2 data to a PC via USB streaming. OBD2 interfaces are typically used in advanced car diagnostics and OEM vehicle development. Further, CAN interfaces that support OBD2 requests can exist useful equally function of contrary applied science proprietary CAN bus parameters.
OBD2 loggers: Used to log OBD2 information from a motorcar to an SD carte du jour - ideal for e.g. blackbox use cases or prototype field tests past automotive OEMs. As an example, the CANedge1 lets yous log Tin omnibus information, likewise equally request OBD2 data past sending custom frame requests to the Tin bus.
WiFi OBD2 logger: WiFi OBD2 loggers and WiFi OBD2 dongles enable the automated transfer of OBD2 data via WiFi (incl. 3G/4G) to a server/cloud. WiFi OBD2 loggers are typically used for OBD2 telematics use cases, where automobile fleet data needs to be collected automatically and visualized via OBD2 data dashboards. For example, the CANedge2 lets yous log CAN/OBD2 data and auto-push it via a WiFi accces point to your ain server. The data can be candy in gratis software tools and e.yard. visualized in Grafana dashboards.

The CANedge2 makes it easy to log OBD2 data to an SD card - and upload it via WiFi to your own server.
Demand to log/stream OBD2 data?
Go your OBD2 information logger today!
Recommended for you
Source: https://www.csselectronics.com/pages/obd2-explained-simple-intro
0 Response to "A C System Vehicle Inspection Obd Reading"
Post a Comment